03 - Tokens, revisions
Overview
- Description:: revisions on general concepts, tokens!
Revision
- double spending let users spend twice a currency
- the ledger is ordered: transactions are sequentially stored
- PoW in Bitcoin forces node to prove computational effort to publish new blocks
Decentralization
- the minimum transaction to activate pieces of code is 1
- The blockchain is NOT a database: it doesn’t store every single account, it only stores transactions
Tokens
- tokens are not cryptofuel, nor anything conceptually new, after all!
- it is like flying miles
- private vs public

- permission means private? NO
- permissionless means private? NO
The different kinds of web
- web 1.0 is just client-server architecture
- I ask things, I receive things
- web 2.0 always client-server but both of them perform requests and responses
- web 3.0 the front is always the same, the backend has interesting features (like smart contracts)
Do i need blockchain?
- not everything, not for everywhere
Models
- Birch model → no
- steem → social media for example, if I get enough upvotes I get token, that I convert in cryptos that I can convert in money

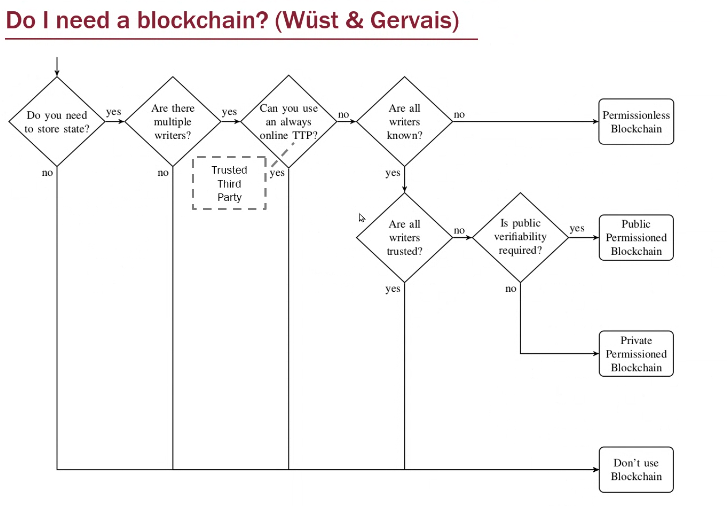
- …
Revising
Graphs
- graphs are structures consisting of
- nodes
- arcs connecting nodes
- directed graphs has directed arcs → we always assume graphs to be directed, unless specified otherwise
- two nodes are adjacent if at least an arc exists that is incident on them
- a node is a successor of another node if an arc exists that is directed from the former to the latter
- a path is a walk such that arcs are never traversed twice
- a cycle is a loop (first node = last node)
Unicycle graphs: chain
Bits nibbles and boring stuff
- nibble is a sequence of 4 bits
- byte is a sequence of 8 bits
Hashing
hashing is a function that associates k to values.
Token vs crypto
- crypto is the euro
- token is the bubbles, flowers, whatever
We can resell tokens in terms of money. I can buy some flowers coins in euros
The blockchain IS NOT a software, is NOT a computer, is NOT a software system
This is why different blockchains exist.
General definitions
- ledger is a collation of transactions
- mining nodes are the subset of nodes that maintain the blockchain by publishing new blocks
- transaction are added to the blockchain when a mining node publishes a block
- a block collates transactions
- transactions are stored and sorted in block
- validity is ensured by checking that
- input accounts have signed the transaction
- input accounts have sufficient funds on their account
- the block timestamp (needs deep revision)
- the other mining nodes WILL NOT accept a block if it contains any invalid transactions!